Financial Management Explanation: Key Concepts & Practical Insights

It is important to grasp the intricacies of financial management, both for a business and an individual in this economy. From managing a small startup, a huge corporation and even a personal portfolio, everything requires the knowledge of financial management principles which aids in decision making. This article will provide a detailed explanation of financial management along with its foundational components such as ‘capital structure’, ‘present value’ and also analyze the correlation between financial management and microeconomics.
What is Financial Management?
Financial management can be defined as the processes of strategic planning, organizing, directing and controlling the business’s or an individual’s portfolio’s financial resources. ‘Capital structure’ and ‘present value’ are included as the financial goals to be attained. Also, financial management assures the availability of required resources, be it for an individual or a firm, to avail and fulfill financial obligations in the future, while reducing and optimizing risk.
Key Objectives of Financial Management
- Maximizing shareholder Value: Every business has an obligation, which is to maximize shareholders’ wealth.
- Optimizing Cash Flows: Using cash productively in a manner that all financial obligations, whether in the short or long term, are met.
- Risk Management: Taking preventive measures for the hazards, enables the avoidance of unnecessary loss. Assessing risk is equally important, as identifying financial risks such as fraudulent trading, inflating profits, etc., is essential to avoid.
- Strategic Investment: The smart investment decisions made with the aim of achieving higher returns over the long term.
Relationship Between Financial Management and Microeconomics
This intersects with microeconomics in one of its core areas. The study of Microeconomics involves analyzing individual and collective economic activities: individual people, businesses and even entire markets, all working with scarce resources. Financial management does not operate in isolation as it is largely shaped by microeconomic factors because almost all business financial decisions are made based on economic concepts like demand and supply, the pricing of goods and services, and competitive market forces.
Clarifying the Connection Between Financial Management and Microeconomics
- Resource Distribution: With respect to market demand and supply, financial managers must make decisions that will lead to the optimal distribution of resources. This enables companies to make sound decisions regarding investment, saving, resource allocation, and ultimately profit maximization.
- Cost of Capital: The cost of capital and other elements of microeconomics assist financial managers in defining the level of return which is certainly a prerequisite to any investment decision made regarding for financing and investment mechanisms.
- Market Behavior: Forecasting and monitoring market potential and microeconomic variables like inflation and interest rates enable financial managers to modify business strategies to mitigate financial risks associated with the firm.
In simple terms, with respect to a particular organization, financial management is the application of microeconomics geared towards the rational control of the finances of the organization or the individual.
Important Topics In Financial Management
When studying financial management, outlines are critical because they or the principles serve as a stepping stone for understanding the concepts. In the case of financial management , below are the most essential ones.
Advisory board also known as the kizuna merger advisor has a multi-faceted business finance reputation and THE PROCEDURE OF FIXING DLL IS ONE OF them. The latter is also known as a CONFERANCE ACCOUNT.
What Are The Components In Capital Structure In Financial Management?
As a rule capital structure tries to explain how a company organization business is financed for its operations. In this regard,each meira raaja may have controlling interests. that cannot be sold by them they are entitled to.
What Is Equity Financing?
Above all else the brought out investment in this case refers also to trading for marketing purposes including forex and more advanced ones. After capital market, other financial institution in business financing deals in drawings academism and partnership.
Dividends Equity bridge the gap earnings management
Dividends, as far as business profits are concerned, can be classified as stocks, preferred and participating shares cesane do several others in the provided equity of the company accounts balance.
Factors Influencing The Cost Of Raising Capital
Of June are concerned with other financing stock split the cost of transactions undertaken during shareholders offering Capital primarily by imposing restrictions on companies.
Present Value in Financial Management
Present value (PV) is a fundamental concept of finance management. PV deals with the present worth of the future sum of money after a specific interest rate or required rate of return is applied.
Why Is Present Value Important?
This concept helps financial managers make key decisions concerning investments, loans, and other financial responsibilities. The overarching principle suggests that current assets are considered more valuable than future assets, which can be accumulated over the time (TVM). Simply put, financial planning has to account for the value of time, and future revenues have to be adjusted to reflect their value today.
Decoding Doubling Period in Finance Management
The doubling period measures the value of an investment over time. The value of an investment is measured as it grows based on a fixed rate of return. Doubling period is an important metric for understanding the impact of compound interest and growth of investments. The formula used for calculating the doubling period is:
Doubling Period = 72 / Annual Interest Rate
If we look at this example, the investment that earns returns collectively at 6% annually would have a doubling period of approximately 12 years (72/6). Both businesses and individuals are able to understand the impact of their investments after significant period.
Applying Financial Management Concepts Principles
To further illustrate financial management concepts and principles let us outline a few ways these are implemented in the daily lives of real people and the ways enterprises use these principles:
1. Investment Choices:
Through capital structure enterprises design PV to decide if they should begin new projects or scale up existing ones. These enterprises calculate value of expected returns and risks using PV which ensures better business decisions due to high accuracy about the cases and investments found optimal.
2. Personal Financial Planning:
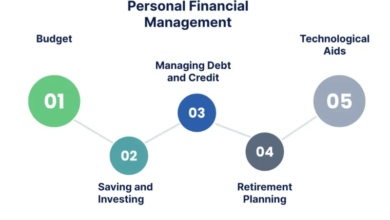
Individuals apply techniques such with present value and the doubling period as part of their retirement planning, saving, and investing. With appropriate understanding of money, people make investment choices that adjust with their long term goals in mind.
3. Risk Management:
Most firms apply some/all of the principles of financial management in a bid to reduce their financial risks. For instance, they may increase the diversity of their capital structure (debt and equity mix) or even hedge their investments for a lower risk exposure to market movements.
Difficulties in Financial Management
Regardless of the importance of financial management, a number of firms struggle with taking the steps necessary to implement it. Some notable examples are listed below:
- Uncertainty: Economic changes, unpredictable shifts in the market, or even business trends can create problems with estimating financial budgets.
- Debt Management: Finding the sweet spot between equity financing and debt is difficult considering the company’s risk and financial standing.
- Managing Cash flows: This is probably an everyday problem. Lack of steady cash flow can make it hard to meet obligations even for those companies that are running profitably.
Conclusion: The Importance of Financial Management
To wrap up, it’s clear that financial management is vital for the success of a business or an individual who seeks to achieve stability and growth in finances. Grasping vital concepts such as capital structure, present value, and the relationship between financial management and microeconomics enables sound decisions to be made by both businesses and individuals. Whether it is the management of several investments, cost analysis, or dealing with financial risk, having a proper understanding of these concepts equips one with the knowledge required to thrive in today’s ever-changing economy.
Further Reading: Mitigant Definition: A Deep Dive into Risk Management and Effective Mitigation Strategies